Phage Display Antibody Library Construction
Overview
Phage display is a powerful approach to isolate antibodies with desired binding properties. At Antibody Design Labs, we have an extended expertise with the construction of phage display antibody libraries in varied formats, sizes, and display systems.
-
Immunized, naive, semi-synthetic, synthetic libraries.
-
Sizes up to 1011 primary transformants
-
Choice of vector, tags, and helper phage (M13KO7, CM13, CM13d3).
-
Choice of format, scFv, VHH, Fab, scaffold.
-
QC by Sanger Sequencing, NGS analysis available upon request.
-
Display analysis by Western blot.
-
Custom deliverables (phage, frozen cell stocks, plates).
Applications
Immunized Murine Fab Library
Phage display enables the discovery of murine antibodies that are not accessible by classical hybridoma technology. We will immunize mice of varied genetic background with your antigen; the spleen of the best responder will be harvested and used to amplify cDNA and build the library. These libraries have a typical size of 1 x 109 clones and mirror the animal immune response. We use our published universal phage display (pUP) system for a seamless construction (Fig. 1). The simultaneous cloning of the VL and the VH generates highly diverse libraries without chain biases with a cloning efficiency >95% per chain.
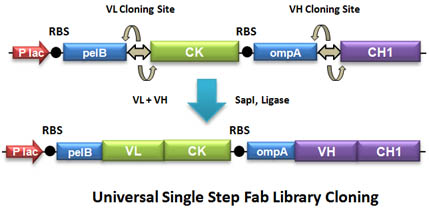
Figure 1. Fab Library Cloning in pUP display system. The universal pUP vector, amplified VL and VH domain are ligated in a single cloning step to generate highly diverse Fab libraries with no bias toward light chains or heavy chains and large coverage of the antibody response (Nelson 2017).
Immunized scFv Library
scFv libraries can be generated from multiple species (mouse, rat, dog, sheep, chicken, …). scFv are well-displayed on the phage, giving stable libraries that are easy to screen.
Synthetic and Semi-Naive Libraries
A number of methods are available to generate synthetic DNA fragments, from parallel synthesis to the use of trimer-codons. Antibody domains can also be assembled from scratch with randomization (hard, soft, tailored) at given positions or CDRs. We also have experience in assembling synthetic DNA fragments with natural fragments to create semi-naive, semi-synthetic libraries, in particular to generate the CDR-H3 (Fig. 2).
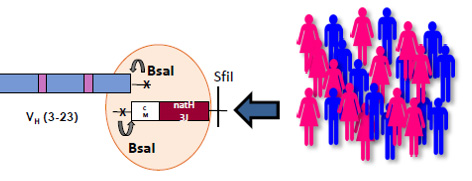
Figure 2. Replacement of H3J Fragments in semi-naive libraries. During the construction of the ALTHEA Gold libraries, the CDR-H3J fragments were derived from a poll opf 200 human donors, this preventing known issues, stickiness in particular, associated with synthetic CDR-H3 (Valadon 2019).
Very Large Fab Library
Fab libraries are notoriously difficult to build because of the need to control diversity and expression of both the light chain and the heavy chain. Thanks to our proprietary phagemid and the universal cloning system described in Fig. 1, we can build Fab libraries in the 1010 range with more than 95% cloning efficicency for each chain.
Naive Single Domain Antibody Library
Llama are a great source of single domain VHH, but the combination of immunization, library construction and screening make these projects very long. On the contrary, naive libraries can be screening in a matter of days, thus bypassing the immunization step. We partner with large farms in the US to collect large pools of llama PBMC and offer the construction of royalty-free naive single domain antibodies as a service.
Request a Quote
Please, request a quote by completing the online quotation form accessible by pressing this button; you will be contacted back by the next business day. All our work is performed by highly experienced staff at our San Diego facility in California. All products and services are for research use only and not intended for use in humans.
For all other inquiries, contact us by email at info@abdesignlabs.com or by phone at 1-877-223-3104 (PST). We guarantee competitive pricing.
References
- Nelson, R.S., & Valadon, P. (2017). A universal phage display system for the seamless construction of Fab libraries. J Immunol Methods, 450, 41-49.
- Valadon, P. et al. (2019). ALTHEA Gold Libraries™: antibody libraries for therapeutic antibody discovery. MAbs, 11(3):516-531.

